7 Ways to Diagnose ALS


ALS can be very difficult to diagnose since there isn’t a specific procedure or test to ultimately establish the ALS diagnosis.
It is only through several diagnostic tests (often used to rule out other diseases that mimic ALS) and a thorough clinical examination that a diagnosis can be established.
According to the ALS Association, a comprehensive diagnostic workup includes most, if not all, of the following procedures:
1 – Electrodiagnostic tests

Electrodiagnostic tests may include electromyography (EMG) to evaluate the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles, and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) – also called nerve conduction study (NCS) – to determinate the speed of conduction of an electrical impulse through a nerve.
2 – Blood and urine
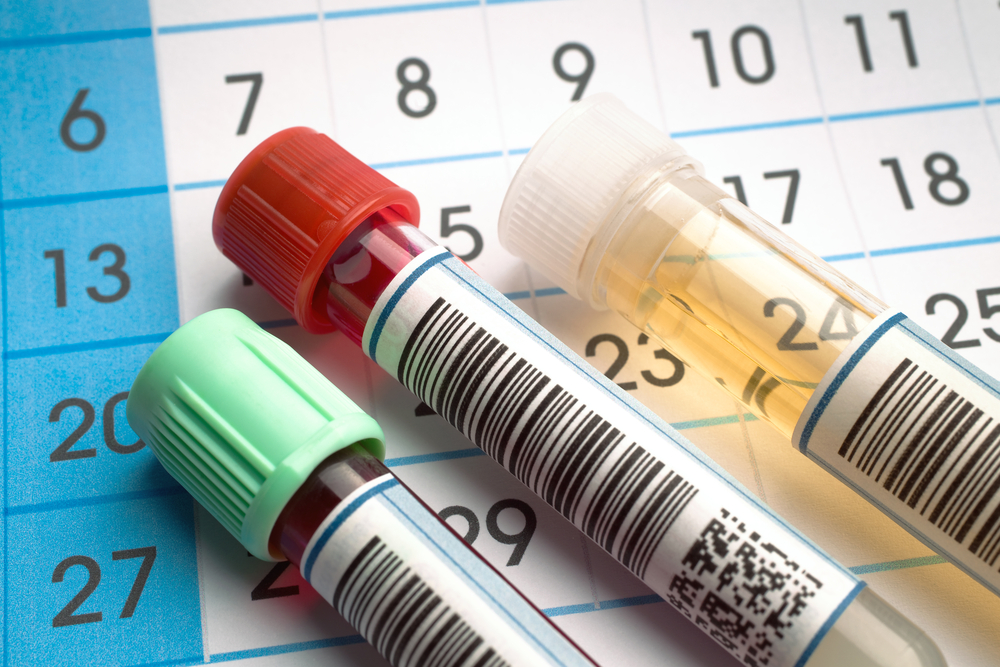
Blood and urine tests may include high-resolution serum protein electrophoresis, thyroid and parathyroid hormone levels, and 24-hour urine collection for heavy metals.
3 – Spinal tap

A spinal tap is a medical procedure also known as a lumbar puncture and is used to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) which surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
4 – X-ray and MRI
These kinds of tests may include x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to look for signs in the bone and organ structures.
5 – Myelogram of cervical spine
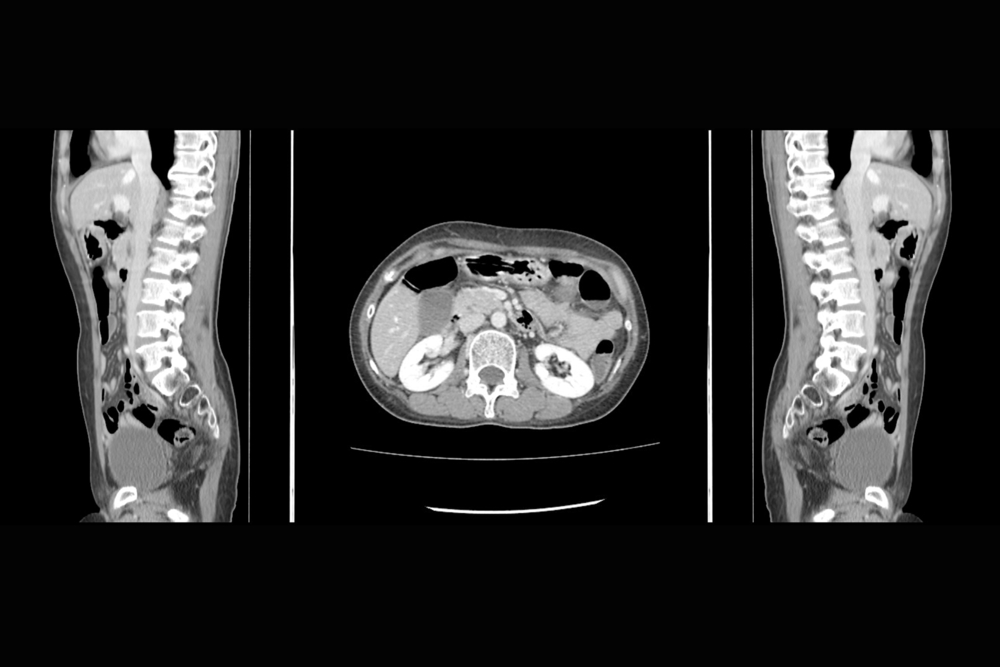
Myelogram of a cervical spine, an imaging procedure that uses a contrast dye and X-rays, or computed tomography (CT).
6 – Biopsy
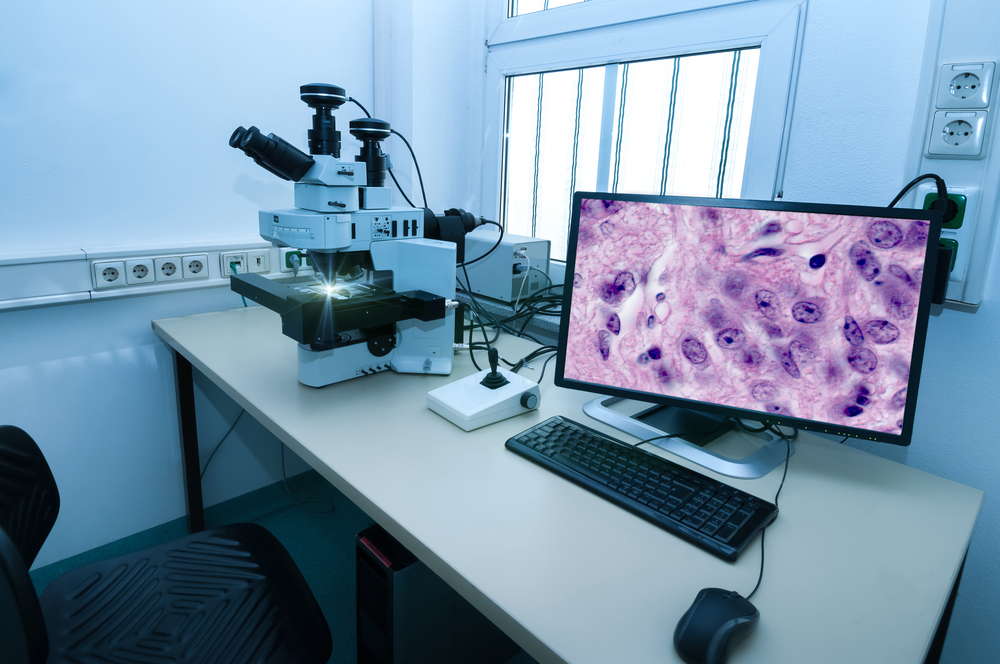
A biopsy may include a muscle and/or nerve sample tissue to examine more closely.
7 – Neurological Examination
A thorough neurological examination in order to do an assessment of sensory neuron and motor responses, especially reflexes, to determine whether the nervous system is impaired.